All About Hair Loss
Learn about the Anatomy of your Hair & Common Myths.
Hair is simple in structure, but has important functions in social functioning, and the FUE Doctors are experts in this field.
Knowledge is King, we will help educate you so you make the best decision for yourself…
Hair is simple in structure, but has important functions in social functioning. Hair is made of a tough protein called keratin. A hair follicle anchors each hair into the skin. The hair bulb forms the base of the hair follicle. In the hair bulb, living cells divide and grow to build the hair shaft. Blood vessels nourish the cells in the hair bulb, and deliver hormones that modify hair growth and structure at different times of life.
The most common form of hair loss is known as Androgenetic Alopecia. This is a hereditary condition passed to you from either of your parents and can affect men or women. It usually affects hair on the top and front of the scalp, but would not normally affect the sides or back, leaving what is normally a “horseshoe” growth on the scalp.
The Hair Anatomy
Hair is simple in structure, but has important functions in social functioning. Hair is made of a tough protein called keratin. A hair follicle anchors each hair into the skin. The hair bulb forms the base of the hair follicle. In the hair bulb, living cells divide and grow to build the hair shaft. Blood vessels nourish the cells in the hair bulb, and deliver hormones that modify hair growth and structure at different times of life.
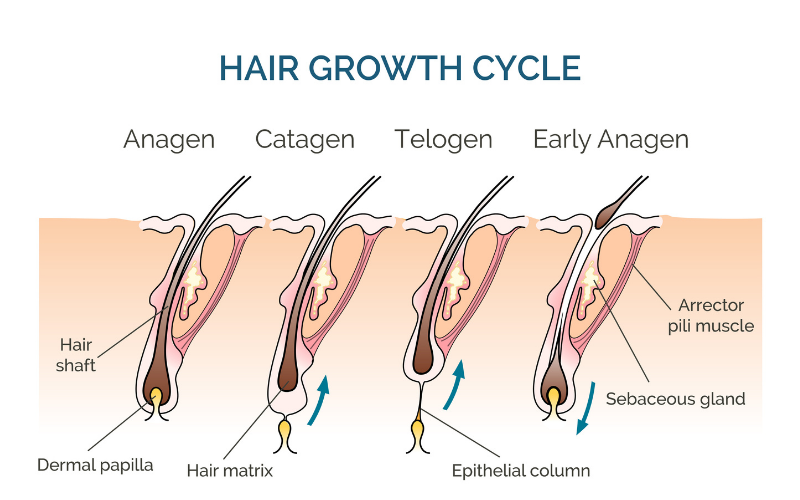
Hair growth occurs in cycles consisting of three phases:
- Anagen (growth phase): Most hair is growing at any given time. Each hair spends several years in this phase.
- Catagen (transitional phase): Over a few weeks, hair growth slows and the hair follicle shrinks.
- Telogen (resting phase): Over months, hair growth stops and the old hair detaches from the hair follicle. A new hair begins the growth phase, pushing the old hair out.
Hair grows at different rates in different people; the average rate is around one-half inch per month. Hair colour is created by pigment cells producing melanin in the hair follicle. With ageing, pigment cells die, and hair turns grey.
The most common form of hair loss is known as Androgenetic Alopecia. This is a hereditary condition passed to you from either of your parents and can affect men or women. This gene usually affects hair on the top and front of the scalp, but would not normally affect the sides or back, leaving what is normally a “horseshoe” growth on the scalp.
Persons with this condition produce a hormone known as Dihydro-testosterone (DHT) that causes the hair follicle to miniaturise, which in turn attracts a reduced blood supply. Over time, these conditions cause the hair and eventually the follicle to die, leaving no chance for hair to regrow.